From counter-terror to Operation Sindoor, Army achieves key milestones in 2025
“Operation Sindoor reflected India’s zero-tolerance policy towards terrorism”
Suhail Khan
New Delhi, Dec 30: As 2025 draws to a close, the Indian Army has marked a transformative year characterised by decisive operational actions, significant technological upgrades, and a continued push towards self-reliance.
The date shared by the defence officials highlights ten major milestones that have collectively enhanced India’s defensive and offensive capabilities while reinforcing its stance on cross-border terrorism.
Central to this year’s operational successes was Operation Sindoor, launched in May following the terror attack in Pahalgam.
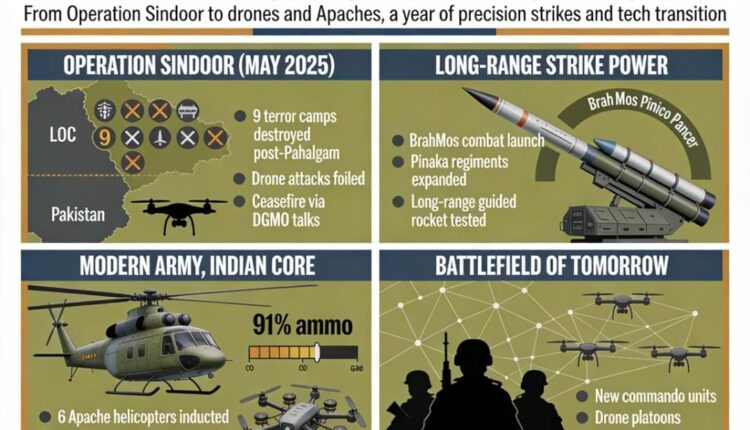
The operation, coordinated by the Military Operations Branch and monitored in real-time by the Chief of Defence Staff and Service Chiefs, neutralised nine terrorist camps across the border. Ground forces destroyed seven camps, while the Indian Air Force eliminated two others.
The action dismantled over a dozen terror launch pads along the Line of Control and countered subsequent Pakistani drone attacks, culminating in a ceasefire request from Pakistan on May 10. Operation Sindoor reflected India’s zero-tolerance policy towards terrorism while demonstrating controlled escalation and strategic resolve.
In parallel, the Army accelerated its firepower modernisation. In December, a BrahMos unit conducted a combat launch, affirming readiness for high-speed precision strikes. The Pinaka rocket system was augmented with two new regiments and the successful test of a 120-km Long Range Guided Rocket. Future variants are expected to provide greater reach, significantly enhancing deep-strike capabilities.
Capability gaps were addressed with the induction of six AH-64E Apache attack helicopters into the Army Aviation Corps. Three arrived in July and the remainder in December, adding mobile firepower and anti-armour support for ground operations.
Structural innovation advanced with the October demonstration of new battlefield organisations, including Bhairav Battalions (light commando forces), Ashni Platoons (drone-based ISR units), Shaktibaan Regiments, and Divyastra Batteries equipped with UAVs and loitering munitions. Together, these units represent a shift towards agile, technology-integrated warfare.
The Army declared the past two years as “Years of Tech Absorption”, achieving a 91 per cent indigenisation rate in ammunition and inducting over 3,000 Remotely Piloted Aircraft, 150 tethered drones, and swarming and logistics drones. The Defence Acquisition Council cleared systems such as thermal imagers for BMPs and Medium-Altitude Long-Endurance UAVs, focusing on unmanned platforms and night-fighting enhancements.
Operational digitisation progressed with the establishment of Edge Data Centres to accelerate data-to-decision cycles. In-house software initiatives, including ‘Equipment Helpline’ and ‘Sainik Yatri Mitra’ apps, enhanced soldier welfare and logistical efficiency.
Strategic direction was set at the Army Commanders’ Conference in Jaisalmer in October, focusing on Grey Zone Warfare, jointness with sister services, and accelerating Aatmanirbharta to meet evolving threats.
International partnerships were strengthened through bilateral exercises: SHAKTI with France (June–July), YUDH ABHYAS with the US (September), AUSTRAHIND with Australia (October), AJEYA WARRIOR with the UK (November), and DESERT CYCLONE with the UAE (December). These exercises improved interoperability in counter-terrorism, urban operations, and conventional warfare.
The Chanakya Defence Dialogue (CDD) 2025 emerged as the Army’s strategic forum. The event featured a Young Leaders Forum and a keynote podcast by General Upendra Dwivedi, focusing on “reform-to-transform” initiatives for national security and development.
Grassroots innovation was highlighted through Inno-Yoddha 2025–26, which received 89 submissions from within the ranks. Thirty-two ideas were selected for development and fielding, contributing to the Atmanirbhar Bharat mission.
The year’s achievements demonstrate an Army responding decisively to immediate threats while proactively transforming through technology, indigenisation, and structural innovation, positioning itself to secure the nation’s future in a complex security environment.

Comments are closed.